时间序列平滑和异常检测利器:tsmoothie库详解
创作时间:
作者:
@小白创作中心
时间序列平滑和异常检测利器:tsmoothie库详解
引用
1
来源
1.
https://wangzhefeng.com/note/2024/04/12/timeseries-lib-tsmoothie/
时间序列分析是数据分析领域的重要分支,广泛应用于金融、气象、生物医学等多个领域。在时间序列分析中,数据平滑和异常检测是两个核心问题。数据平滑可以帮助去除噪声,揭示数据的内在趋势;异常检测则有助于识别数据中的异常点,为后续分析提供更准确的数据基础。本文将介绍一个功能强大的Python库——tsmoothie,它提供了多种平滑技术和异常检测方法,能够帮助用户高效地处理时间序列数据。
tsmoothie:时间序列平滑和异常检测
tsmoothie是一个Python库,用于向量化方式的时间序列平滑和异常值检测。
- 去噪
- 异常值剔除
- 保留原始数据中存在的时间模式
tsmoothie 平滑技术
tsmoothie使用了多种平滑技术:
- 指数平滑(Exponential Smoothing)
- 卷积平滑(Convolutional Smoothing)
- constant
- hanning
- hamming
- bartlett
- blackman
- 傅里叶变换频谱平滑(Spectral Smoothing with Fourier Transform)
- 多项式平滑(Polynomial Smoothing)
- 样条平滑(Spline Smoothing)
- linear
- cubic
- natural
- 高斯平滑(Gaussian Smoothing)
- 分箱平滑(Binner Smoothing)
- 局部加权回归散点平滑法(LOWESS)
- 季节性分解平滑(Seasonal Decompose Smoothing)
- 卡尔曼平滑(Kalman Smoothing),支持自定义组件
- level
- trend
- seasonality
- long seasonality
LOWESS
局部加权回归散点平滑法(LOWESS)是一种查看二维变量之间关系的有力工具。其主要思想是取一定比例的局部数据,在这部分子集中拟合多项式回归曲线。将局部范围从左往右依次推进,最终一条连续的曲线就被计算出来了。曲线的平滑程度与选取数据比例有关:比例越少,拟合越不平滑(因为过于看重局部性质),反之越平滑。
区间计算
tsmoothie提供了作为平滑过程结果的区间计算,这对于识别时间序列中的异常值非常有用。区间类型包括:
- sigma interval
- confidence interval
- predictions interval
- kalman interval
tsmoothie可以进行滑动平滑的方法来模拟在线使用。这可以将时间序列分成大小相等的部分并独立平滑它们。与往常一样,此功能通过WindowWrapper类以矢量化方式实现。
Bootstrap 算法
tsmoothie可以通过BootstrappingWrapper类操作时序引导,用到的Bootstrap算法有:
- none overlapping block bootstrap
- moving block bootstrap
- circular block bootstrap
- stationary bootstrap
tsmoothie 安装
$ pip install tsmoothie
tsmoothie 使用
tsmoothie 平滑 demo
随机游走数据平滑
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tsmoothie.utils_func import sim_randomwalk
from tsmoothie.smoother import LowessSmoother
# 生成3个长度为200的随机游走数据
np.random.seed(123)
data = sim_randomwalk(
n_series = 3,
timesteps = 200,
process_noise = 10,
measure_noise = 30,
)
# 平滑处理
smoother = LowessSmoother(smooth_fraction = 0.1, iterations = 1)
smoother.smooth(data)
# 生成区间
low, up = smoother.get_intervals("prediction_interval")
# 绘制平滑后的时序数据及其区间
plt.figure(figsize = (18, 5))
for i in range(3):
plt.subplot(1, 3, i + 1)
plt.plot(smoother.smooth_data[i], linewidth = 3, color = "blue")
plt.plot(smoother.data[i], ".k")
plt.title(f"timeseries {i + 1}")
plt.xlabel("time")
plt.fill_between(
range(len(smoother.data[i])),
low[i],
up[i],
alpha = 0.3,
)
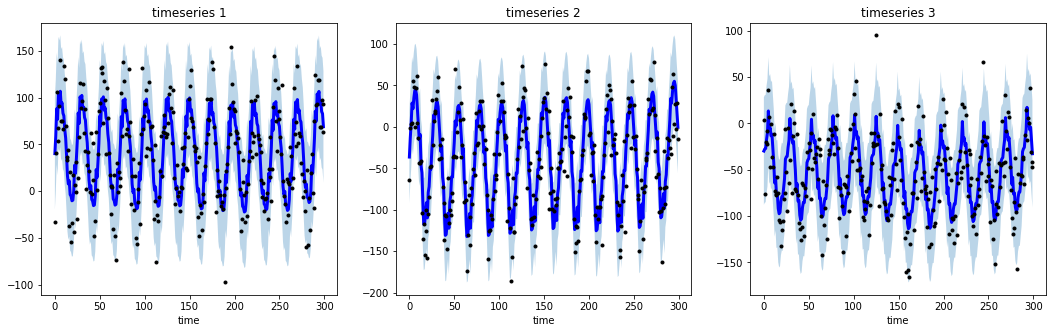
季节性数据平滑
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tsmoothie.utils_func import sim_seasonal_data
from tsmoothie.smoother import DecomposeSmoother
# 生成3个周期性时序数据
np.random.seed(123)
data = sim_seasonal_data(
n_series = 3,
timesteps = 300,
freq = 24,
measure_noise = 30
)
# 平滑处理
smoother = DecomposeSmoother(
smooth_type = 'lowess',
periods = 24,
smooth_fraction = 0.3
)
smoother.smooth(data)
# 生成区间
low, up = smoother.get_intervals('sigma_interval')
# 绘制平滑后的时序数据及其区间
plt.figure(figsize = (18, 5))
for i in range(3):
plt.subplot(1, 3, i + 1)
plt.plot(smoother.smooth_data[i], linewidth = 3, color = 'blue')
plt.plot(smoother.data[i], '.k')
plt.title(f"timeseries {i+1}")
plt.xlabel('time')
plt.fill_between(
range(len(smoother.data[i])),
low[i],
up[i],
alpha = 0.3
)
tsmoothie Bootstrap demo
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tsmoothie.utils_func import sim_seasonal_data
from tsmoothie.smoother import ConvolutionSmoother
from tsmoothie.bootstrap import BootstrappingWrapper
# 生成周期性时序数据
np.random.seed(123)
data = sim_seasonal_data(
n_series = 1,
timesteps = 300,
freq = 24,
measure_noise = 15
)
# Bootstrap处理
bts = BootstrappingWrapper(
ConvolutionSmoother(
window_len = 8,
window_type = 'ones'
),
bootstrap_type = 'mbb',
block_length = 24
)
bts_samples = bts.sample(data, n_samples = 100)
# 绘制Bootstrap后的时序数据
plt.figure(figsize = (13, 5))
plt.plot(bts_samples.T, alpha = 0.3, c = 'orange')
plt.plot(data[0], c = 'blue', linewidth = 2)
时间序列平滑以更好地聚类
时间序列平滑以更好地预测
降低传感器中的噪声以更好地预测太阳能电池板的发电量
时间序列数据
- 房子每天的煤气消耗量,$m^{3}$
- 房子每天的用电量,$kWh$
- 负值表示太阳能超出了房子的用电量
- 直流转交流转换器上功率计的日值。这是当前累积的太阳能发电量。不需要累积值,而是需要绝对的每日值,因此,进行简单的微分操作。这是预测的目标
时间序列数据平滑
Kalman Filter
时间序列异常检测
极端事件的时间序列预处理
深度学习中的时间序列 Bootstrap
参考
←GluonTS
热门推荐
冬季跑步训练:如何选购最适合的跑鞋?
我发现能长久的关系,伴侣身上都有这1个特征
具备世界一流的技术水平,日本90式主战坦克
《情书》电影深度解析:一段跨越时空的情感之旅
2024年高考前心态调整
人工智能艺术与人类艺术--人们更喜欢哪一种?
如何撰写出色的求职信
平顺龙门寺
新手如何养蝴蝶兰
洋房和高层的区别在哪里
光合作用的意义与发生机制
解锁摄影潜能:全面解析相机镜头的选择与使用逻辑
小儿盗汗的原因、症状与治疗方法全解析
过去与现在:社会变迁的对比分析
20多万条企业大数据背后:上海制造为何仍有竞争力
坟地里埋骨灰盒是否违法?法律解读与实务分析
内线篮球防守的最佳策略:从站位到团队配合的全面指南
机器人与“脊髓假体”首次无缝集成,可恢复瘫痪者运动能力
排除合理怀疑:刑事犯罪司法实践中的关键问题探讨
玄之又玄,众妙之门—谈中国古代玄学演变史
笔记本电脑GPU天梯攻略:全面解析与主流GPU对比
合理使用数智技术,为师生有效减负
双刃剑-双氧水在脑外科的应用
来龙兴古镇 触摸时光记忆
宝宝起名指南:创意与寓意两全其美
转债回售全梳理及套利机会分析
CPVC电力管和PVC穿线管的区别详解
完全生物基乙缩醛二环氧单体:模量高、热稳定性好、易降解
2024甲辰年生肖虎流年运势
如何合理规划五险一金的缴纳与使用?这种规划方式有哪些潜在的问题?