使用LLMs从非结构化文本中提取结构化数据
使用LLMs从非结构化文本中提取结构化数据
这是一篇关于使用LLMs从非结构化文本中提取结构化数据的技术文章。文章主要介绍了两种方法:使用LangChain代理和Pydantic模型。文章内容详细,包含代码示例和具体实现步骤,对于AI和数据处理领域的专业人士具有较高的参考价值。
用例:使用LLMs提取非结构化竞争情报数据
想象一下你是一个面包店,你已经派出你的糕点师情报团队去收集竞争对手的数据。他们报告了竞争对手的动态,并且他们有很多你想应用到你生意中的好主意。然而,这些数据是非结构化的!你如何分析这些数据以了解最常被要求的是什么,以及如何最好地优先安排你业务的下一步?
代码可在GitHub上获取:注意:代码根据使用的具体工具,被分割成两个文件:unstructured_extraction_chain.ipynb 和 unstructured_pydantic.ipynb。
为了探索这个用例,我创建了一个玩具数据集。以下是数据集中的一个示例数据点:
在Velvet Frosting Cupcakes,我们的团队了解到了季节性糕点菜单的推出,该菜单每月更换。在我们的面包店引入使用“SeasonalJoy”订阅平台的轮换季节性菜单,并使用“FloralStamp”饼干印章为我们饼干添加特殊触感,可以使我们的产品保持新鲜和令人兴奋。
选项1:创建提取链
我们可以先观察数据,通过这样做,我们可以识别出一个粗略的模式——或者说是结构——来进行提取。使用LangChain,我们可以创建一个提取链。
# Inputs
in1 = """Sweet Delights Bakery introduced lavender-infused vanilla cupcakes with a honey buttercream frosting, using the "Frosting-Spreader-3000". This innovation could inspire our next cupcake creation"""
in2 = """Whisked Away Cupcakes introduced a dessert subscription service, ensuring regular customers receive fresh batches of various sweets. Exploring a similar subscription model using the "SweetSubs" program could boost customer loyalty."""
in3 = """At Velvet Frosting Cupcakes, our team learned about the unveiling of a seasonal pastry menu that changes monthly. Introducing a rotating seasonal menu at our bakery using the "SeasonalJoy" subscription platform and adding a special touch to our cookies with the "FloralStamp" cookie stamper could keep our offerings fresh and exciting for customers."""
inputs = [in1, in2, in3]
并创建链
最后,运行链在示例上
现在我们有了作为Python列表的结构化输出:
[{'company': 'Sweet Delights Bakery', 'offering': 'lavender-infused vanilla cupcakes', 'advantage': 'inspiring next cupcake creation', 'products_and_services': 'Frosting-Spreader-3000'}]
[{'company': 'Whisked Away Cupcakes', 'offering': 'dessert subscription service', 'advantage': 'ensuring regular customers receive fresh batches of various sweets', 'products_and_services': '', 'additional_details': ''}, {'company': '', 'offering': 'subscription model using the "SweetSubs" program', 'advantage': 'boost customer loyalty', 'products_and_services': '', 'additional_details': ''}]
[{'company': 'Velvet Frosting Cupcakes', 'offering': 'rotating seasonal menu', 'advantage': 'fresh and exciting offerings', 'products_and_services': 'SeasonalJoy subscription platform, FloralStamp cookie stamper'}]
让我们使用附加参数更新我们的原始数据
这是一个不错的开始,看起来它正在运行。然而,最佳工作流程涉及导入包含竞争情报的CSV文件,将其应用到提取链进行解析和结构化,然后将解析后的信息无缝地整合回原始数据集。下面的Python代码正是这样做的:
import pandas as pd
from langchain.chains import create_extraction_chain
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
# Load in the data.csv (semicolon separated) file
df = pd.read_csv("data.csv", sep=';')
# Define Schema based on your data
schema = {
"properties": {
"company": {"type": "string"},
"offering": {"type": "string"},
"advantage": {"type": "string"},
"products_and_services": {"type": "string"},
"additional_details": {"type": "string"},
}
}
# Create extraction chain
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-3.5-turbo")
chain = create_extraction_chain(schema, llm)
# ----------
# Add the data to a data frame
# ----------
# Extract information and create a DataFrame from the list of dictionaries
extracted_data = df['INTEL'].apply(lambda x: chain.run(x)[0]).apply(pd.Series)
# Replace missing values with NaN
extracted_data.replace('', np.nan, inplace=True)# Concatenate the extracted_data DataFrame with the original dfdf = pd.concat([df, extracted_data], axis=1)
# display the data frame
df.head()
这次运行花了大约15秒,但它还没有找到我们请求的所有信息。让我们尝试另一种方法。
选项2:Pydantic
在下面的代码中,Pydantic被用来定义表示竞争情报信息结构的数据模型。Pydantic是Python的一个数据验证和解析库,允许你使用Python数据类型定义简单或复杂的数据结构。在这种情况下,我们使用Pydantic模型(Competitor和Company)来定义竞争情报数据的结构。
import pandas as pd
from typing import Optional, Sequence
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
from langchain.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from pydantic import BaseModel
# Load data from CSV
df = pd.read_csv("data.csv", sep=';')
# Pydantic models for competitive intelligence
class Competitor(BaseModel):
company: str
offering: str
advantage: str
products_and_services: str
additional_details: str
class Company(BaseModel):
"""Identifying information about all competitive intelligence in a text."""
company: Sequence[Competitor]
# Set up a Pydantic parser and prompt template
parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=Company)
prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="Answer the user query.\n{format_instructions}\n{query}\n",
input_variables=["query"],
partial_variables={"format_instructions": parser.get_format_instructions()},
)
# Function to process each row and extract information
def process_row(row):
_input = prompt.format_prompt(query=row['INTEL'])
model = OpenAI(temperature=0)
output = model(_input.to_string())
result = parser.parse(output)
# Convert Pydantic result to a dictionary
competitor_data = result.model_dump()
# Flatten the nested structure for DataFrame creation
flat_data = {'INTEL': [], 'company': [], 'offering': [], 'advantage': [], 'products_and_services': [], 'additional_details': []}
for entry in competitor_data['company']:
flat_data['INTEL'].append(row['INTEL'])
flat_data['company'].append(entry['company'])
flat_data['offering'].append(entry['offering'])
flat_data['advantage'].append(entry['advantage'])
flat_data['products_and_services'].append(entry['products_and_services'])
flat_data['additional_details'].append(entry['additional_details'])
# Create a DataFrame from the flattened data
df_cake = pd.DataFrame(flat_data)
return df_cake
# Apply the function to each row and concatenate the results
intel_df = pd.concat(df.apply(process_row, axis=1).tolist(), ignore_index=True)
# Display the resulting DataFrame
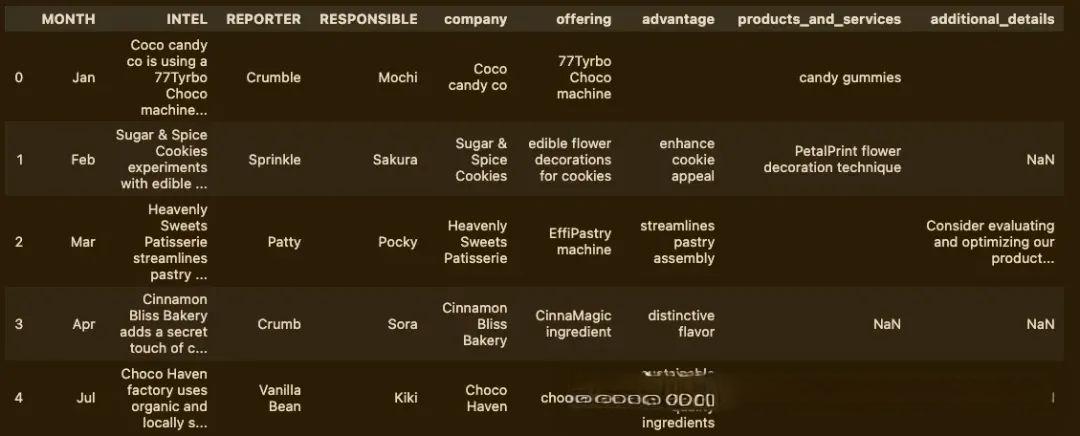
intel_df.head()
这真的很快!而且它找到了所有条目的细节,不像create_extraction_chain尝试那样。
总结
本文介绍了两种从非结构化文本中提取结构化数据的方法:使用LangChain代理和Pydantic模型。这两种方法各有优劣,可以根据具体需求选择合适的方法。这是系列文章的第一篇,后续文章将关注使用LangChain代理分析从非结构化文本中提取的结构化数据。